Remember that a primary feature of Digital Assurance is ensuring smooth interactions between all sorts of devices and platforms. Compatibility testing is a major step towards ensuring such smooth interactions because it prepares the application to be compatible for use across platforms.
Once you are done with Functional Testing, you move on to the non-functional testing part, which includes compatibility testing. This testing is concerned with whether the application can run smoothly across different hardware and software.
Another non-functional type of Omni-Channel Testing is Usability Testing. It revolves around testing how easily end-users can use the system. The process is irreplaceable since it enables brands to gather insights about how real end-users interact with the application.
Digital Assurance focuses on the multi-faceted needs of digital applications, which involves ease of use. This is exactly why Usability Testing is a vital part of Digital Assurance. Always remember that you can make a great application, but no one’s going to use it unless it’s easy to use. No product can be successful without undergoing this step.
This may be the last area under Omni-Channel Testing, but that does not make it any less important. In fact, Security Testing is one of the most important parts. Here, you focus on the security of the application on various platforms.
It does so by refining the main operations and functions of an application. This ensures that the end-user feels no dissonance about what the app is supposed to do and what it actually does.
Why Digital Assurance Matters
Omni-Channel Performance Testing helps uncover how reliable your application is, even when used on several different devices. Here, you will simply check the responsiveness, speed, and stability of your application on different devices.
1. Need for Agility
Customers of any product need to feel comfortable and safe enough to share information online without worrying about whether their data is in the right hands or not. And that is exactly what Digital Assurance comes in.
2. Increased Customer Satisfaction
All in all, Omni-Channel Functional Testing sets the groundwork for Digital Assurance.
3. Decreased Security Threats
A common challenge at this stage is to address mobile device fragmentation. Mobile device fragmentation is when some mobile users continue using an older OS version while some update to using the newer one. In such cases, you have to test that the application is compatible with all versions of an OS.
How Digital Assurance and Omni-Channel Testing Relate
The digital ecosystem is a complex environment. In such an environment, leveraging different components to provide customer satisfaction becomes difficult. Digital Assurance involves aiding interactions between various components of a product or application, and it helps deliver optimum performance. This, in turn, results in greater customer satisfaction.
- Decreases security risks and safeguards customer data
- Ensures an ideal customer experience
- Helps companies adapt to change
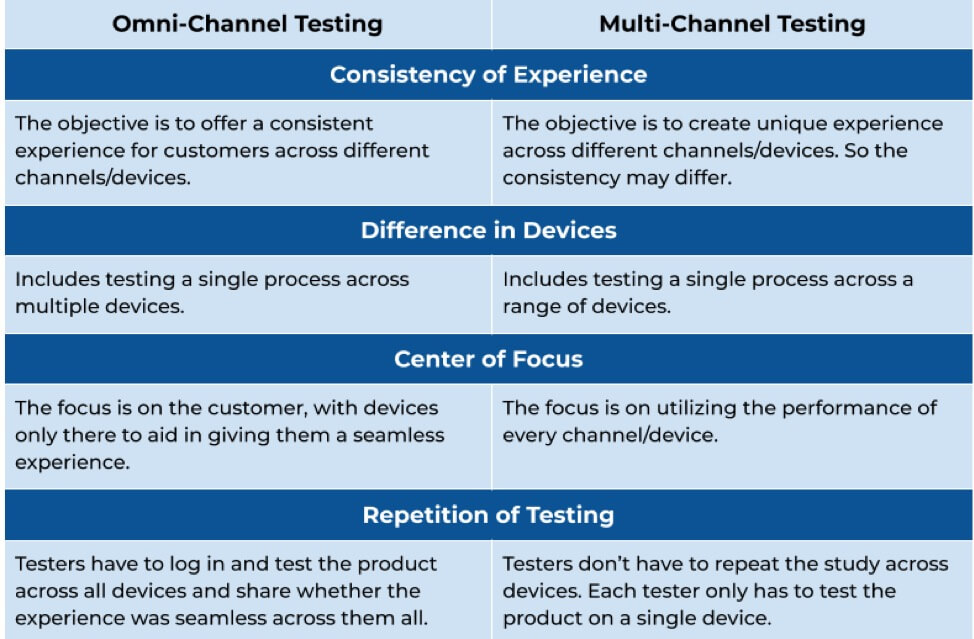
The main difference between the two lies in the process that is to be tested. If you have to test the functionality of a product or application across various channels/devices, use Multi-channel Testing. Here, the focus is on the functionality of the product. However, if you have to test the user experience of a product or application across various channels/devices, use Omni-Channel Testing. The focus here is on how effective the user finds the product.
To start off, you gather a group of possible end-users and ask them to perform some tasks using your application. You then observe their interactions and notice areas where they encountered problems or were confused. Also, notice the frequency of these problems – if more and more people face a similar issue, then ask for recommendations on how to improve the application. At the end of it all, ask for suggestions and feedback on what works and what doesn’t.
The answer is: through testing. The only way to create more agile digital systems with lowered security risks is with more thorough testing to spot and eliminate glitches and bugs. Similarly, without different kinds of testing, companies cannot work towards providing improved user experiences.
What is Omni-Channel Testing?
We’ve all heard the saying “Knowledge is power.” This is now truer than ever, as customer information is the most valuable asset a company has. While the digital ecosystem brings with it many opportunities for growth, it also brings the threat of security breaches. Configuring and testing, both parts of Digital Assurance, help decrease these threats.
Each application has an initial design, and hopefully, the end result is close to that initial design. Performance Testing is where you find out whether the application performs as it was designed to or not.
Difference between Omni-Channel and Multi-Channel Testing
While there are myriads of reasons why companies should adopt Digital Assurance, here are just a few important ones.
Companies exist within a greatly dynamic digital landscape. With continually changing processes and new assurance initiatives, companies need to have adaptability. This is just another way of saying companies need to be agile. Digital Assurance helps ensure agility, since it provides companies with a solid foundation of data security and user information protection, thereby allowing brands to act quicker and bolder when new opportunities show up on the horizon.
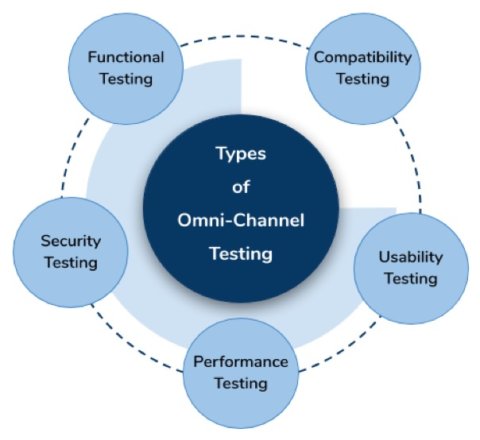
Types of Omni-Channel Testing & How They Facilitate Digital Assurance
Omni-Channel Testing comprises of a total of five subtypes. Let’s see what these are.
1. Omni-Channel Functional Testing
A major aim of performance testing is ensuring a better customer experience. As we mentioned at the very beginning, the ultimate result of Digital Assurance is supposed to be just that – a better customer experience. This is exactly why performance testing is such a vital step in the entire process.
- Mainline functions and features of the application
- Basic usability of the application to check how freely an end-user can navigate between screens
- Testing error conditions to ensure that appropriate error messages are displayed
- Checking the ability of the application to work together with diverse systems and organizations
- Administering and managing computer networks and ensuring networks maintain their quality of service
What most software developers do is that they create different versions of the same application. Each application version supports a different version of the mobile OS. While this increases the work of the developers, it helps ensure that the application runs effectively across all platforms.
2. Omni-Channel Compatibility Testing
With more and more companies now looking to provide a holistic assurance strategy, the Digital Assurance Market keeps growing. No surprise then that it is expected to reach .86 billion by 2026.
This involves uncovering any vulnerabilities in the application that could become problematic in the future. Go over the entire application with one question in mind, “Can a hacker hurt the application in any way?”. It also includes ensuring that all data entered in the application and flowing through it is safe from intruders.
Everything in today’s day and age is being digitized. However, the growth of digitization and automation comes at a cost – in this case, that cost is the security (or lack thereof) of the end-user’s personal information. With the rise of technology catering to almost all customer needs, there is also a rise in the demand for customer safety.
3. Omni-Channel Usability Testing
Keep in mind that data is power and all applications contain valuable user data. This is why your application is susceptible to attacks from hackers. While you may think you’ve built a completely secure product, you need to undergo Omni-Channel Testing to find the real vulnerabilities still present in the system.
Companies need to assure end-users that their personal information is not being misused. This isn’t just limited to data safety. It envelops all quality assurance practices that ensure smooth interactions between various components of Digital Ecosystems. The ultimate result of implementing Digital Assurance is an improved customer experience.
4. Omni-Channel Performance Testing
Here’s what we’ve learnt about Digital Assurance so far:
The question now is, how do all these benefits translate into actionable processes?
5. Omni-Channel Security Testing
Omni-Channel Testing revolves around testing an application or product across various devices and platforms. The aim is to ensure that the user experience is seamless and consistent across all the platforms. This assurance of seamless user experience is a major part of the overarching field of Digital Assurance.
As Shawndra Hill pointed out, Digital Assurance is all about teaching companies how to keep their data safe. That is what this crucial step of the Omni-Channel Testing journey is accomplishing. It is the final cornerstone towards ensuring that customer data is safe within the final application.
The Omni-Channel Testing Way of Launching a New Product:
Wharton professorShawndra Hill described it best when she said, “Digital assurance is about educating companies and consumers on how they can keep their data secure.”
Omni-Channel Testing involves several areas of testing that are important for your application to be a success. Starting from the functional aspect of your product to its ease of use and performance, Omni-Channel Testing covers it all.
Apart from this, there are also several other differences between the two types of testing, as we can see below.