Query categories for which Google will seek out fresh content include:
The freshness factor doesn’t exist in a vacuum. Rather, it’s one of the multiple factors or trust signals that both search algorithms use for ranking and users contemplate before clicking any of the results. And since freshness is more relevant to certain queries than others, the requirement for fresh content should always be evaluated on the basis of your primary keyword.
- What content freshness is and how it’s measured.
- When content freshness is a ranking factor.
- How to know when it’s time to refresh content.
- How to improve your freshness score.
What is fresh content?
Fresh content refers to recently published, updated, or rewritten content. Google and its users appreciate fresh content because it’s more likely to be accurate.
So let’s take a look at your options when freshness is crucial or important.
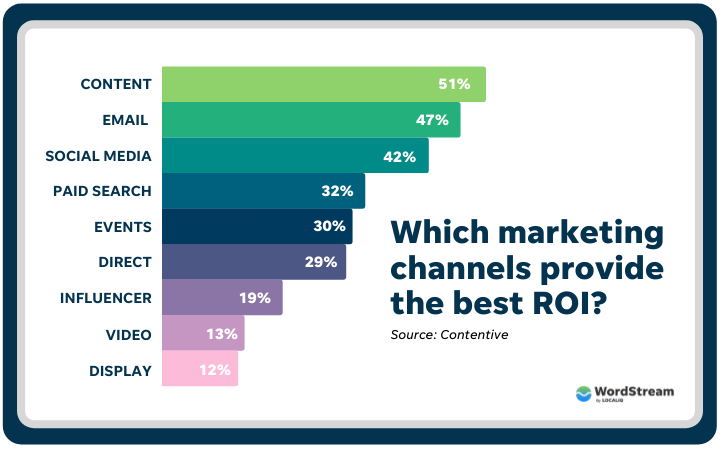
We commonly hear that having fresh content can help your SEO, but it’s not as common for us to see a breakdown of exactly what fresh content means and how important it is for ranking.
- Published: when the page was uploaded on the website.
- Indexed: when the crawlers first discovered the page and added it to Google Search.
- Last crawl: when the page was last crawled by those bots.
- Modified: when the last change was made to the page.
Moz, Google estimates the freshness of your content based on many factors, including:
- Page inception date: The date it was indexed by Google.
- Amount of change to the updated page: Large changes signal more freshness.
- Number of changes to core content of the page: Changes to the main body content add more freshness than adjusting the date/time tags.
- Rate of page change: Frequent changes on the page signal more freshness.
- Rate of new page creation: Websites that add new pages more frequently may get a higher freshness score.
- Freshness of backlinks to the page: Links from sites that have high freshness scores can improve yours.
Image source
Is content freshness a Google ranking factor?
The easiest way to evaluate the level of freshness that users presumably want for a query is to look at the publication dates of the top results. For example, you can check the first 10 or 20 results and calculate their average age. Ideally, you should also give more weight to the top-ranking results in your calculation.
Fresh vs “unfresh” queries
We covered a lot in this post, so let’s finish off with a recap:
- Recent events (e.g. a playoff game)
- Hot topics (e.g. Google’s page title update – trending at the time of this post).
- Recurring events and reports (e.g. presidential elections, annual conferences).
- Ongoing but always-changing information (e.g. product reviews).
Now that we established how content freshness can impact ranking for time-sensitive queries, let’s quickly go through some tips and best practices for incorporating the freshness factor into your SEO strategy.
- Food recipes
- Historical facts
- Broad topics
- Evergreen topics
This method is best for evergreen topics that resonate with your audience long-term; as well as pages for which you want to preserve backlinks and other beneficial SEO traits.
In his SEO Blueprint training course, Glen Allsopp stresses the importance of aligning the published time Google associates with your URL with the year in your page title.
Articles where the published time doesn’t match the year in the title are, in fact, fairly common.
search marketing
is and what it covers, which hasn’t really changed in the last few years.
gains new backlinks continually but is not updated can certainly compete with a newer page that doesn’t have inbound links or keeps losing its existing links.
How to improve your freshness score: best practices
Whenever republishing revised articles, it’s a good idea to share them on social media, just as you would any other new article to boost engagement.
1. Check the SERP
Fresh queries
Google research publication points out that search engines cannot recrawl every page all the time due to the massive scale of new content being published every day.
Following these metrics for your content over time will provide useful insights into your page performance and whether there’s a need for updates or revisions. You can track these metrics using Google Analytics or by pulling the data to a spreadsheet with a reporting tool like Supermetrics (as in the image below)
Someone interested in reading about ecommerce trends will likely be looking for the latest trends in the ecommerce industry, not those of the previous years.
engagement metrics, that certainly can have a negative impact on your ranking.
6. …and then actually change the publish date
Let’s take a look at some examples.
Here is what Ahrefs suggests:
rank it higher depends on how important freshness is for your query.
While Google pays more attention to major updates, minor updates to a page are still important, because as we mentioned, a page’s freshness deprecates over time, no matter how evergreen. Examples of small updates include:
- When freshness is crucial: Update the page frequently or publish new articles on the topic regularly to keep up with demand.
- When freshness is important but not critical: Update the page regularly, and if ranking starts to drop, consider revising and republishing.
- When freshness isn’t important: Focus on creating the best possible guide on the topic.
For example, at Supermetrics, we cover affiliate marketing trends every year. If you search for “affiliate marketing trends,” none of the results on the first or second page are older than from 2020.
When to update content
This method is a great way to get more traffic from your evergreen posts that don’t need major revisions.
- Adding in new internal links
- Updating platform screenshots
- Adjusting headings
- Adding a new item to a list
A good example of topics that require new content regularly is any article that lists out and explains trends around a certain theme.
When to revise and republish content
Pro tip: Another option is to combine several topically related, outdated articles into one updated ultimate guide and redirect all traffic from the old pages to the new one. Especially if those old pages are performing well, you don’t end up losing that existing traffic, either.
Revising outdated posts/pages and changing the published date is an effective way to boost freshness. This becomes relevant when an article requires a complete overhaul to meet visitors’ need for recent, up-to-date content. It should earn you a higher freshness score than a simple update.
Sprout Social
.
Ever since its freshness algorithm update in 2011, queries for trending or time-sensitive keywords trigger Google to prioritize newer pages with the most up-to-date information. The freshness update impacted at least one result on the page for 35% of searches.
So in this post, we’re going to cover:
When to publish new content
Query categories where recency has no major impact on the accuracy of the information may include:
By updating old content regularly, you improve your freshness score which can then make it easier for your time-sensitive content to rank.
learn more SEO metrics here.
We can identify four dates associated with any URL that has been published online:
attract links organically, all of which is a signal to Google that your page deserves to be at the top of the search results.
As a result, Google crawls pages preferentially based on their rate of content update.
- Freshness is a ranking factor for Google but only for pages that target time-sensitive and trending queries.
- If recency adds little or no value to the query you are targeting, frequent updates won’t help your page to outrank an older, authoritative result.
- The best way to determine how important freshness is for a particular keyword is to search that query and look at the top 10-20 results.
- If freshness is important, monitor your page performance and update your content only when its ranking starts to decline.
- Depending on the performance metrics, you can decide whether to update the page regularly, revise and republish it, or create entirely new content on the topic.